

News of the Day
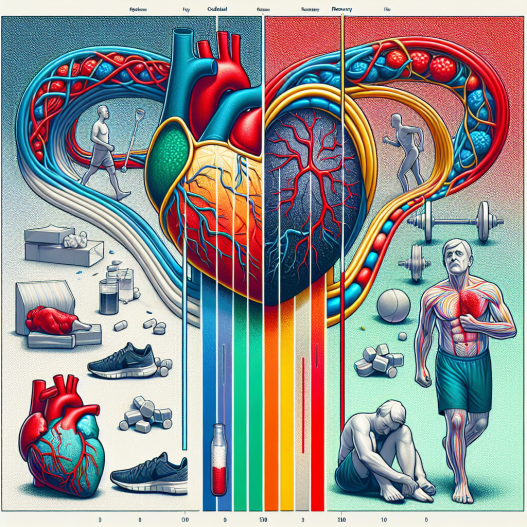
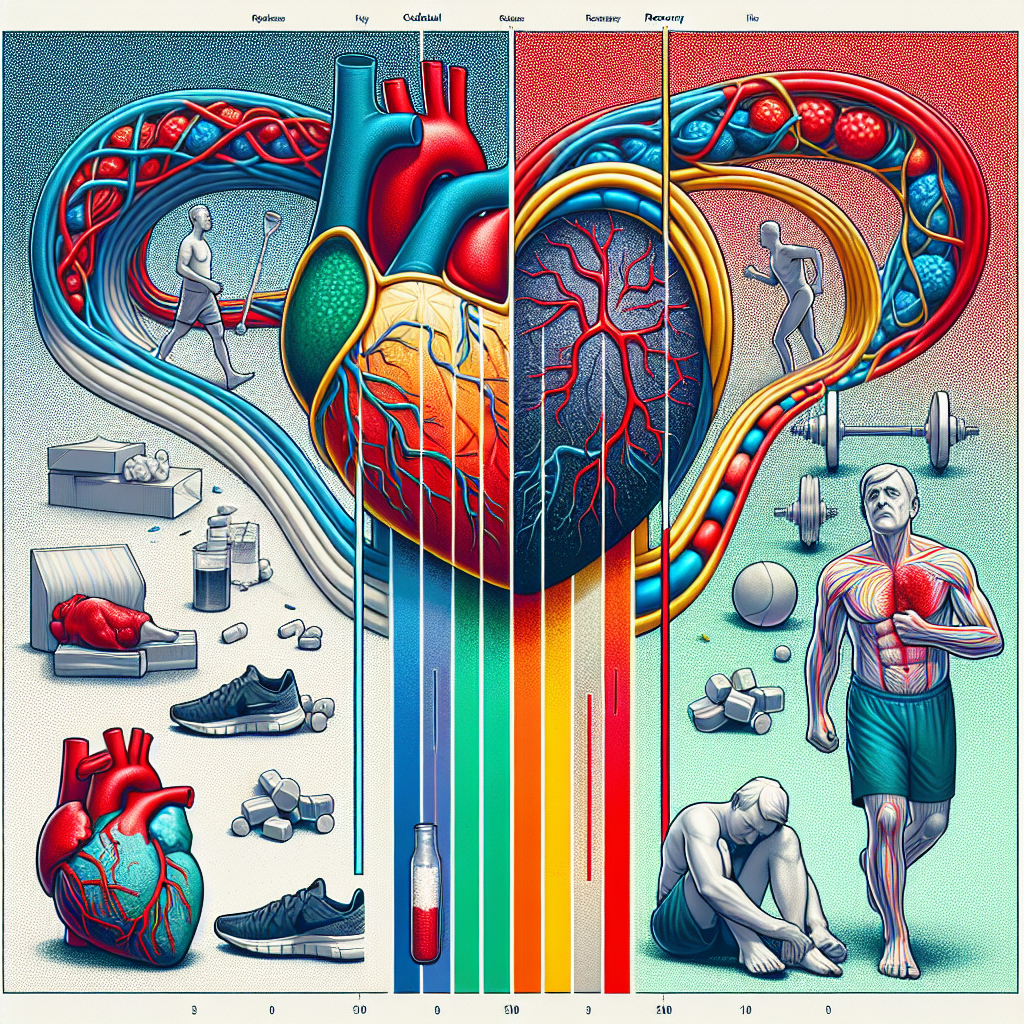
Cholesterol levels and recovery after physical exercise: correlations to consider
Discover the correlations between cholesterol levels and recovery after physical exercise. Learn how exercise can impact your cholesterol levels.
November 9, 2025
Most Popular
Cholesterol and athletic performance: an overview
Learn about the relationship between cholesterol and athletic performance in this comprehensive overview. Discover how cholesterol affects your fitness goals.
November 9, 2025
November 8, 2025


November 7, 2025
November 7, 2025


November 5, 2025
November 4, 2025
Latest Posts
October 30, 2025
October 29, 2025
October 28, 2025
October 27, 2025
October 27, 2025
October 26, 2025
October 26, 2025
Most Discussed
October 25, 2025
October 23, 2025